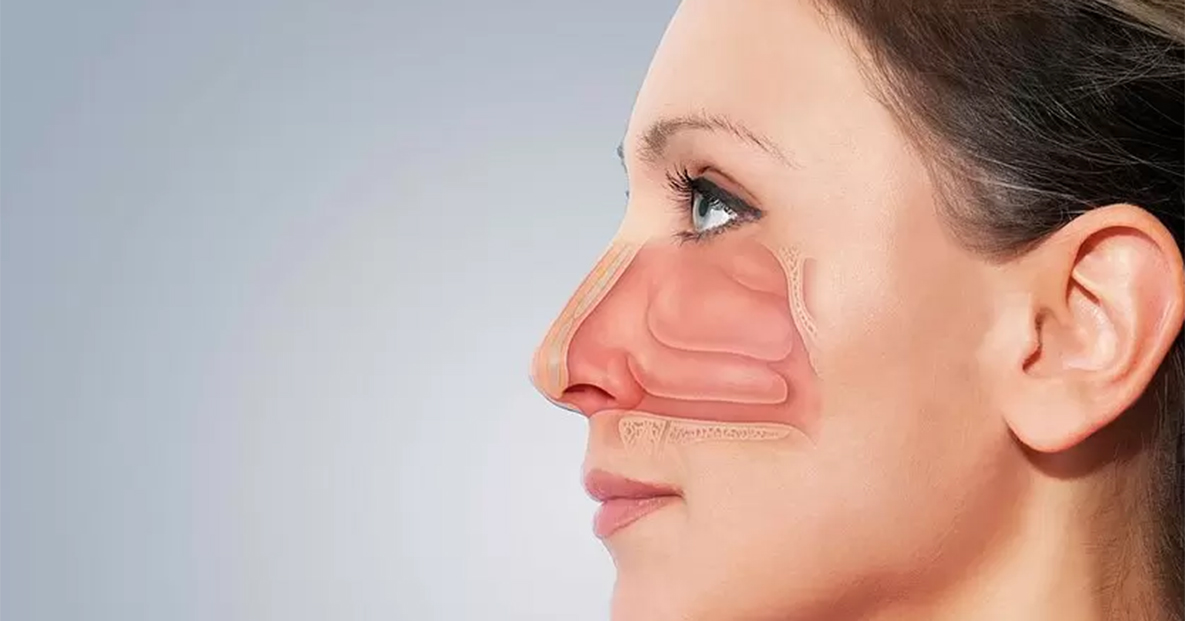
Diode Laser improves quality of ENT surgery
(Staff Reporter)
5 June 2010
DUBAI – Laser surgeries for the ear, nose and throat (ENT) are gaining popularity in the UAE.
Laser is now universally accepted as the most advanced technological tool in various specialities of surgery. However the properties of all lasers are not alike and surgeries in the ENT field have advanced significantly with the introduction of Diode Laser.
It offers the most bloodless surgery available today. This laser is especially suited for ENT works and finds application in various aspects of surgery in the ear, nose, larynx, neck etc. With introduction of Diode Laser, there has been a significant improvement in the quality of ENT surgery.
The commonly used lasers in ENT till date were CO2 (carbondioxide), argon laser and Nd: YAG laser. The diode laser, 980 nm wavelength which was invented and introduced to the field of ENT surgery recently, combines the beneficial effects of all these lasers into one. The tissue cutting effect is comparable to that of CO2 laser, its coagulation effects are comparable to that of argon laser, and it results in a slightly higher degree of absorption by tissue than does the ND: YAG laser.
“As in all surgeries, precision is of utmost importance. In ENT surgery a lot of work especially operation on the ear, vocal cords and now tonsils and adenoids are undertaken using the microscope,” says Dr Udaya Chand Das, ENT Specialist, Zulekha Hospital who introduced this surgery for the first time in a private hospital in 2009.
“The microscope provides a well illuminated and magnified operative field in which the bright red laser is positioned with great accuracy. The laser beam can have precision up to even 0.1 mm or less facilitating super fine work during surgery,” he says.
He also says the laser beam will seal of all small blood vessels automatically as it cuts during surgery. “This is of great importance as the blood loss is minimized, avoiding blood transfusion and associated risks,” he adds. The diode laser can be delivered through a 200 micrometer flexible fibre. This is of vital importance where access is limited as in children and in small operating areas such as ear and vocal cords.
“By its property of sealing of blood vessels and lymph vessels immediately, the spread of cancer cells during operation is significantly reduced. Many open major surgeries can be avoided when the cancer is treated with the laser. The laser beam works by instant vaporization of the tissue. This reduces the post operative swelling and therefore a quicker recovery with less pain for the patient,” he says.
Diode laser can be used for outpatient indications like turbinate reduction, nasal obstruction, polyps, septal surgery, LAUP for snoring, tonsillectomy, oral lesions, leukoplakia, bleeding from nose etc.
Inpatient indications are mainly endoscopic sinus surgery, tonsillectomy, vocal cord lesions, vaporization of papillomas and vaporization of tumours (in larynx and pharynx), DCR etc.
Endoscopic surgery is an established, modern process in the treatment of nasal and paranasal sinus diseases. However, due to the strong bleeding tendency of the mucosal tissue, surgical treatment in this area is often challenging. A poor operating field of vision due to bleeding often results in imprecise work; prolonged nasal packing and significant patient and doctor effort
is usually unavoidable. The main imperative in endonasal surgery is to maintain the surrounding mucosal tissue as much as possible. Due to the ideal laser-tissue interaction of the 980nm wavelength, adjacent tissue is protected optimally. This leads to rapid re-epithelialisation of
bone areas that had been opened up. As a result of the good haemostatic effect, precise procedures can be undertaken with a clear view of the operating area. Using the fine and flexible biolitec optical laser fibers with core diameters of up to 220μm, optimal access to all nasal areas is guaranteed.
– Nasal muscular hyperplasia
– Septal spur, septal deformation
– Epistaxis, Morbus Osler
– Synechias, stenoses in endonasal structures
– Concha bullosa
– Paranasal surgery
– Polyposis nasi et sinuum
– Cysts, mucoceles
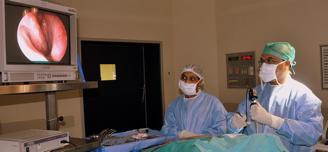
Dr Das performing Laser assisted FESS
– Microsurgical precision
– Minimal post-operative swelling of tissue
– Bloodless operation
– Clear view of operating field
– Minimal operative side effects
– Outpatient operation possible under local anesthesia
– Short recovery period
– Optimum preservation of surrounding mucosal tissue
One of the must frequent operations in the oropharynx area is laser tonsillotomy in children (KISSING TONSILS). In paediatric symptomatic tonsillar hyperplasias, LTT represents a sensible, gentle and very low risk alternative to tonsillectomy (children up to 6 years of age). The risk of post-operative bleeding is minimal. The minimal amount of post-operative pain thanks to the shortened period of healing, the ability to perform out-patient operations (with general anesthesia) and the leaving behind of a tonsillar parenchyma are significant advantages to laser tonsillotomy. Laser-assisted uvulopalatoplasty (LAUP) can be performed for snorers using the EVOLVE™ system. Due to the ideal laser-tissue interaction, tumours or dysplasias can be removed bloodlessly while keeping the adjacent tissue unaffected. A partial GLOSSECTOMY can only be done under general anesthesia in a hospital operating room.
– Tonsillotomy and Tonsillectomy.
– Laser assisted Uvolopalatoplasty (LAUP)
– Partial glossectomy
– Tumour vaporization
– Outpatient operation possible
– Minimal invasive, bloodless Procedure
– Short recovery time with little postoperative pain
Hindered drainage of tear fluid, caused by a blockage of the lacrimal duct, is a common condition, particularly amongst older patients. The traditional treatment method is to surgically reopen the lacrimal duct externally. However, this is a lengthy, difficult procedure associated with a high potential for side effects such as strong, post-operative bleeding and scar formation.
biolitec has developed a patented application set for DCR that makes the reopening of the lacrimal duct a safer, minimally invasive procedure. The thin cannula with its atraumatically shaped mandrel is introduced once in order to perform the treatment pain-free and bloodlessly. Then, the required drainage is set in place using the same cannula. The procedure can be done under local anesthesia and leaves no scars.
– Atraumatic procedure
– Limited complications and side effects
– Local anesthesia
– No infection, no scar.
– No post-operative bleeding or oedema formation
With its extremely thin laser fiber (220μm), the EVOLVE™ system can be used safely and very precisely on delicate structures in the inner ear using the contact method. In contrast to the CO2 laser using the open beam method, this method almost completely eliminates the risk of laser energy inadvertently affecting other areas. The laser energy is only applied upon laser contact with the target tissue and in very short impulses, resulting in the absorption of all of the laser energy immediately at the tip of the fiber. The thermal damage depth is thus at a minimum.
Laser paracentesis is a minimally invasive bloodless operation which has the advantage of the opening in the eardrum made by the laser remaining open for about 3 weeks. The healing process is much
– Stapedectomy
– Myringotomy (Paracentesis)
The main imperative in surgical treatments in the larynx area is to avoid significant scar formation and undesired tissue loss since this can significantly affect phonetic functions. The pulsed diode laser application mode is used here. This way, the thermal penetration depth can be further reduced; tissue vaporization and tissue resection can executed precisely and in a controlled manner, even on sensitive structures, while optimally protecting the surrounding tissue.
– Papilloma
– Laryngeal cancer
– Strictures
– Cordectomy
– Arytenoid cartilage vaporisation
– Epiglottectomy

Dr Das performing Laser Microlaryngeal Surgery.

Preparation of optic fibre for laser
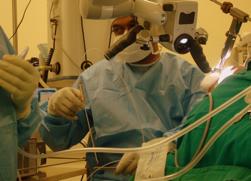
Firing laser before use
(This article is adapted from www.biolitec.de)
Copyright @ 2023 | All Rights Reserved by : DAS ENT Care